Vaginal Itching: Causes, Remedies and Prevention
Vaginal itching, including the discomfort associated with an itchy vagina, is a common concern among women, and it’s essential to address it effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments for an itchy vagina. Whether you’ve experienced this discomfort for a short time or an extended period, understanding the underlying factors and seeking appropriate medical advice is crucial for your overall health and well-being.
What Is Vaginal Itching?
Vaginal itching, also known as vulvar itching, refers to the discomfort or irritation in the vaginal and vulvar area. While occasional itching is normal and often due to harmless causes, persistent or severe itching, such as that experienced with an itchy vagina, may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
What Causes Vaginal Itching?
1. Chemical Irritants
Everyday products like scented soaps, bubble baths, feminine sprays, vaginal douches, fabric softeners, and colored toilet paper can contain chemicals that may cause allergic reactions and itching when they come into contact with the sensitive genital area.
2. Diabetes and Urinary Incontinence
Women with diabetes or urinary incontinence may experience itching due to the irritant effect of urine on the skin.

3. Yeast Infections
Approximately 50-60% of women will experience thrush (yeast infection) at least once in their lives. Thrush is characterized by symptoms like soreness, vaginal and vulvar itching, thick, paste-like discharge, redness, discomfort during intercourse, and small white spots in the vulva or vagina. In 10% of cases, Candida Glabrata, a less common Candida species, causes the infection, resulting in thin gray discharge and irritation.
4. Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
Bacterial vaginosis is the most frequently encountered vaginal infection in women between puberty and menopause. The precise cause of BV remains uncertain, but it results from an overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria in the vagina. These anaerobes, which thrive without oxygen, are countered by the beneficial lactobacilli in the vaginal environment. Lactobacilli help maintain vaginal acidity, preventing the proliferation of anaerobes and, subsequently, the development of BV.BV reduces vaginal acidity, usually maintained by lactobacilli-produced acidic discharge. An increase in vaginal alkalinity promotes anaerobe growth, leading to BV. Common BV symptoms include excessive discharge with a fishy odor and skin irritation when the discharge contacts the vulva. Fortunately, BV is typically treated to relieve its unpleasant symptoms, as it poses no other harm to the body. For more information about Bacterial Vaginosis read “Bacterial Vaginosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments”
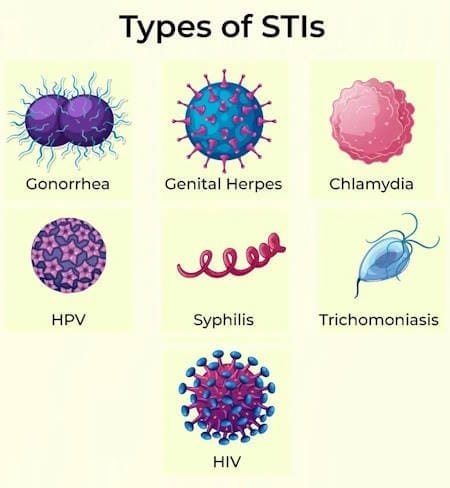
5. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Various sexually transmitted diseases can lead to vaginal burning, itching, and discomfort.
- Chlamydia: Often asymptomatic but may cause vaginal irritation, urethritis, and cervicitis. It can lead to severe pelvic infections if left untreated.
- Genital Herpes: Characterized by painful genital ulcers, with primary infections more severe than recurrent ones. Burning, itching, and discomfort are common symptoms.
- Genital Warts (HPV): Warts may appear months after infection, causing uncomfortable burning and itching. Infection with certain HPV subtypes can lead to vulval malignancy.
- Trichomonas: Symptoms include discharge, itchiness, pain during urination, and a burning sensation within the vagina.
- Gonorrhea: Associated with cervicitis, it causes unusual vaginal discharge, irritation, and frequent discomfort during urination.
6. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections often manifest as painful, irritating sensations and burning during urination. The most common UTI in women is cystitis, which infects the bladder, often caused by bowel bacteria reaching the vagina and ascending into the bladder, typically led by E.coli.
UTIs can worsen in individuals who have used catheters, suffered from other systemic diseases, or experienced infections related to sexual activity or postmenopause. The trigone, the base of the bladder, comprises estrogen-dependent mucosa, making it susceptible to postmenopausal UTI-associated discomfort.
7. Hormonal Changes
Menopausal or perimenopausal women may experience vaginal dryness and itching due to decreased estrogen levels.
8. Puberty
Girls who have not yet reached puberty may experience itching because of lower estrogen levels.
9. Skin Conditions
Skin diseases like eczema, psoriasis, or lichen sclerosis can affect the genital area and cause itching. Vulvar Lichen Sclerosis is an inflammatory skin condition affecting the vulva, characterized by severe inflammation, skin thinning, itching, burning, and other painful symptoms. While its exact cause is unknown, it may have an immune basis and is sometimes associated with autoimmune disorders like thyroid conditions. Vulvar lichen planus is an inflammatory skin disorder affecting the vulva and sometimes the vagina. It is less common on the vulva but can cause significant discomfort, including itching, burning, and pain.
10. Vulvar Cancers
Although rare, vulvar cancers or precancers can cause persistent itching in elderly women.
11. Parasitic Infections
Infestations such as scabies or pubic lice can also lead to itching in the vulvar region. Pubic lice, often called crabs, are tiny insects that infest the genital area and pubic hair. They spread through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity or, more rarely, via contaminated bed linens, towels, or underwear. Symptoms include itching, visible lice and nits (lice eggs), blood specks on underwear, and dark or blue spots where lice feed.
12. Waxing or Shaving
Waxing or shaving the genital area can lead to pain, irritation, bruising, bleeding, and infection, especially if done improperly or with unhygienic tools. Proper tools, care, and consideration of medical conditions affecting skin fragility are essential. Allergic dermatitis may result from pre-shaving products like foams or gels, leading to extreme genital itching.
Vaginal Itching Before, During or After Periods
Vaginal itching during periods often stems from either hormonal changes or sensitivities/allergies to certain products like tampons.
Hormonal Changes: The vaginal ecosystem maintains a delicate balance of various bacteria and yeasts. Hormonal shifts can disrupt this equilibrium, leading to vaginal itching. Such hormonal changes may occur due to:
- Menstruation
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
Sensitivities and Allergies: Another common cause of vaginal itching during your period is sensitivities or allergies to products that come in contact with the vaginal skin. Some hygiene products that could trigger this itching during menstruation include:
- Sanitary pads
- Tampons
- Soaps and deodorizing sprays
- Underwear made from synthetic fibers
- Underwear laundered with harsh detergents or fabric softeners
It’s important to note that prolonged exposure to a triggering product may exacerbate vaginal itching.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild and short-lived itching may resolve on its own or with simple home remedies, persistent or severe itching accompanied by any of the following symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider:
- Itching lasting more than one week.
- Sores or blisters in the genital area.
- Unusual or foul-smelling discharge.
- Pain or discomfort during urination.
- Redness or rashes that do not improve.
- Greenish or yellowish discharge with a frothy appearance.
- Symptoms of urinary tract infections.
- Changes in urinary frequency.
- Postmenopausal or prepubertal girls with itching.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the underlying cause of vaginal itching and provide appropriate treatment. Depending on the cause, treatment options may include:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial vaginosis and certain sexually transmitted infections, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the underlying infection.
- Antifungal Medications: Vaginal yeast infections can be treated with antifungal suppositories, creams, or oral medications.
- Estrogen Therapy: Menopausal or perimenopausal women may benefit from estrogen creams to alleviate vaginal dryness and itching.
- Topical Steroids: In cases of skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, topical steroid creams may be recommended to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Hygiene and Lifestyle Changes: Practicing good hygiene, wearing breathable cotton undergarments, and avoiding scented products can help prevent irritant-induced itching.
- Home Remedies: Natural remedies such as probiotics, virgin coconut oil, tea tree oil, and boric acid suppositories may offer relief for some individuals.
- Barrier Contraception: Using barrier methods like male or female condoms can help reduce friction and irritation during intercourse.
- Regular Check-ups: For persistent or recurring vaginal itching, consult your healthcare provider to rule out any underlying health concerns.
Preventing Vaginal Itching
Taking proactive steps to prevent vaginal itching is crucial for maintaining optimal vaginal health. Here are some preventive measures:
- Avoid using scented or harsh chemical products in the genital area.
- Maintain good hygiene practices without over-cleaning.
- Wash from front to back after bowel movements.
- Choose breathable, cotton undergarments.
- Use barrier contraception to reduce friction during intercourse.
- Stay well-hydrated and maintain a balanced diet.
- Seek medical attention promptly for any unusual symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What can cause vaginal itching after sex?
Itching around the vulva or vagina after sex can be caused by allergic reactions (such as latex or lubricant allergies), sexually transmitted infections (STIs), vaginal dryness, vaginal infections, or sperm allergies. These factors can all lead to genital itching in females after intercourse.
Which vaginal itching creams are available over the counter for immediate relief?
For immediate relief from vaginal itching, over-the-counter creams like Monistat (Miconazole) and Clotrimazole are effective for yeast infections, while Vagisil provides temporary relief for general itching and irritation. Benadryl Cream (Diphenhydramine) can help with itching due to allergic reactions, and Vagisil Maximum Strength Anti-Itch Cream offers temporary relief with benzocaine as a local anesthetic. Cortizone-10 (Hydrocortisone) is also available for reducing inflammation and itching from minor skin irritations. These creams are easily accessible and can be used without a prescription.
Is vaginal itching normal during pregnancy?
Yes, vaginal itching during pregnancy is common and often caused by hormonal changes that can lead to pH imbalances or yeast infections. It may be accompanied by itching around the urethra, pain, burning, or discharge. These symptoms, while uncomfortable, typically subside after giving birth. If you’re concerned, consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
Can stress cause vaginal itching?
Yes, stress can contribute to vaginal itching. Stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections or flare-ups of skin conditions that cause itching. Managing stress through relaxation techniques may help reduce symptoms.
Final Thoughts
Vaginal itching is a common concern that can range from a minor annoyance to a sign of an underlying issue. While many cases of itching are due to benign causes, persistent or severe symptoms warrant a visit to a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment. By understanding the potential causes, practicing good hygiene, and seeking timely medical care, women can ensure their vaginal health and overall well-being.